

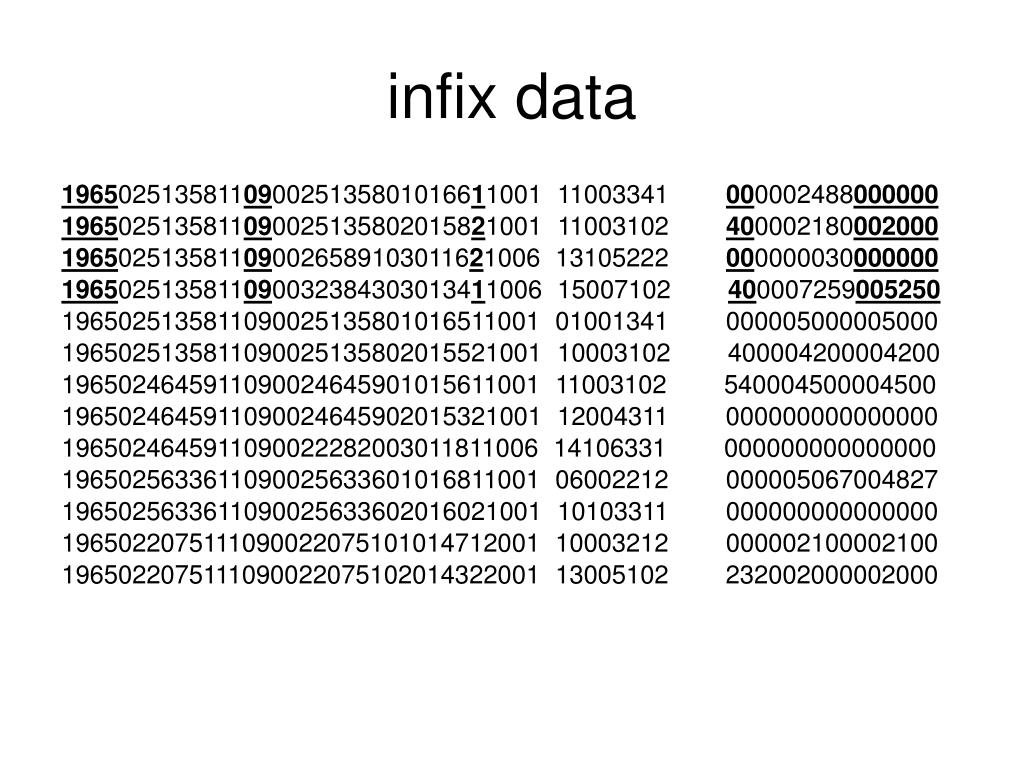
Repeat operation for categories of a variableīriefly describes the data (# of obs, variable names, etc.)Ĭreates new variables (e.g. generate years = close – start) If you do this, then you can re-sort the data after the stem-and-leaf plot according to the index variable (Stata command: sort index ) so that the data is back in the original order.Ĭommands: Here are some other commands that you may find useful (this is by no means an exhaustive list of all Stata commands): anova A command to do so is: generate index = _n However, if you really want to do a stem-and-leaf plot you should always create a variable containing the original observation numbers (called “index”, for example). The best way to avoid this problem is to avoid doing any stem-and-leaf plots (do histograms instead). The “stem” function seems to permanently reorder the data so that they are sorted according to the variable that the stem-and-leaf plot was plotted for. There is a glitch with Stata’s “stem” command for stem-and-leaf plots.
Compute multiple regression equation (vy is response,.Identify points with largest and smallest residuals:.Produce a residual plot with horizontal line at 0:.Compute residuals, create new variable tt residuals:.Produce scatter plot with regression line added:.Compute predictions, create new variable yhat:.Compute simple regression line (vy is response, vx is predictor):.
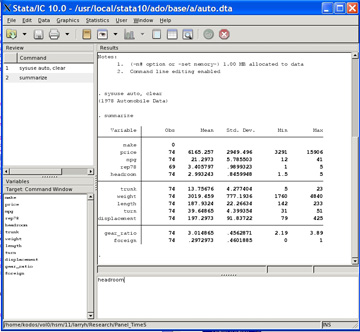
A matrix of scatter plots for three variables:.Plot side-by-side box plots for one variable (vone) by categories of another variable vtwo.Plot a histogram of a variable with a normal approximation:.Plot a histogram of a variable using frequencies:.Today I will teach you Common Stata Commands


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
